Kanban innovation: stock and flow
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a way to make work in progress visible. By tracking, tracing and visualizing the stock (the in- and outflow) the end 2 end process becomes more predictable. The goal of the method is to give feedback in response to an action. It helps to identify and resolve potential bottlenecks in the process, so that the work can be done right the first time (first-time-right) with optimal speed or throughput (just-in-time).
How does it work?
Kanban (from the Japanese ‘kan’, meaning ‘visual’, and ‘ban’, meaning ‘card or board’) signals when something needs to be done.
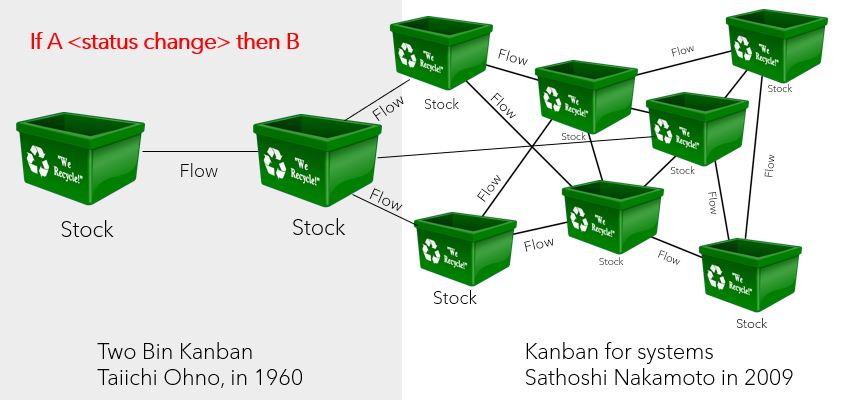
Two Bin Kanban
Taiichi Ohno, 1960 The first Kanban system was developed by #Taiichi Ohno (industrial engineer and businessman) for Toyota in Japan.
Digital System Kanban
Satoshi Nakamoto, 2009 On January 9, 2009, Nakamoto released open source software that allows you to share status updates with pseudonymous actors that you don’t have to rely on.
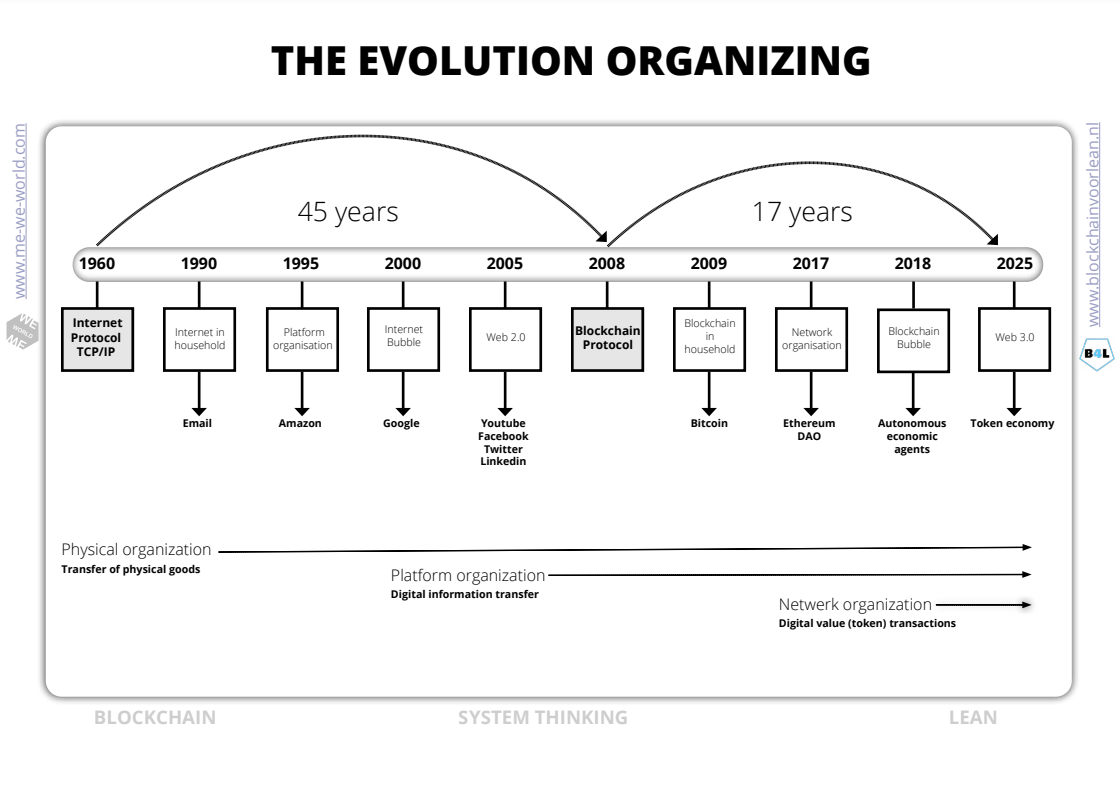
Kanban Innovation
The technology behind this new invention, better known as Blockchain, lends itself well as a collaboration technology to make processes more efficient and effective.
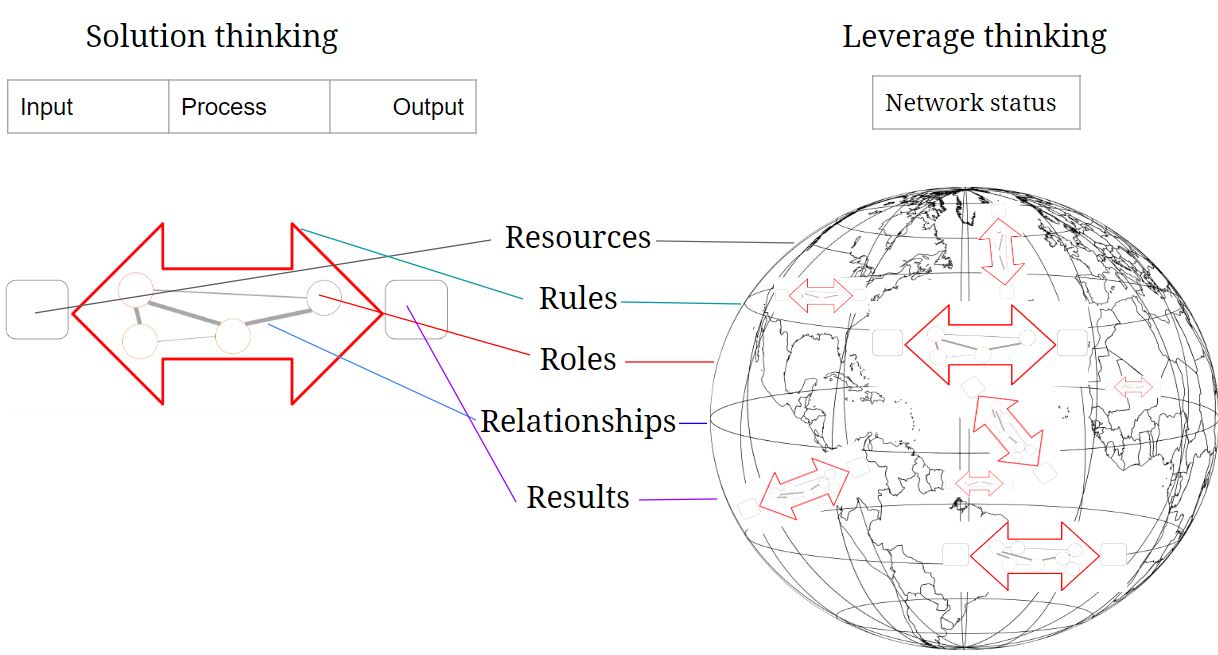
Roles, Resources, Rules, Relationships and Results
Roles/Identity
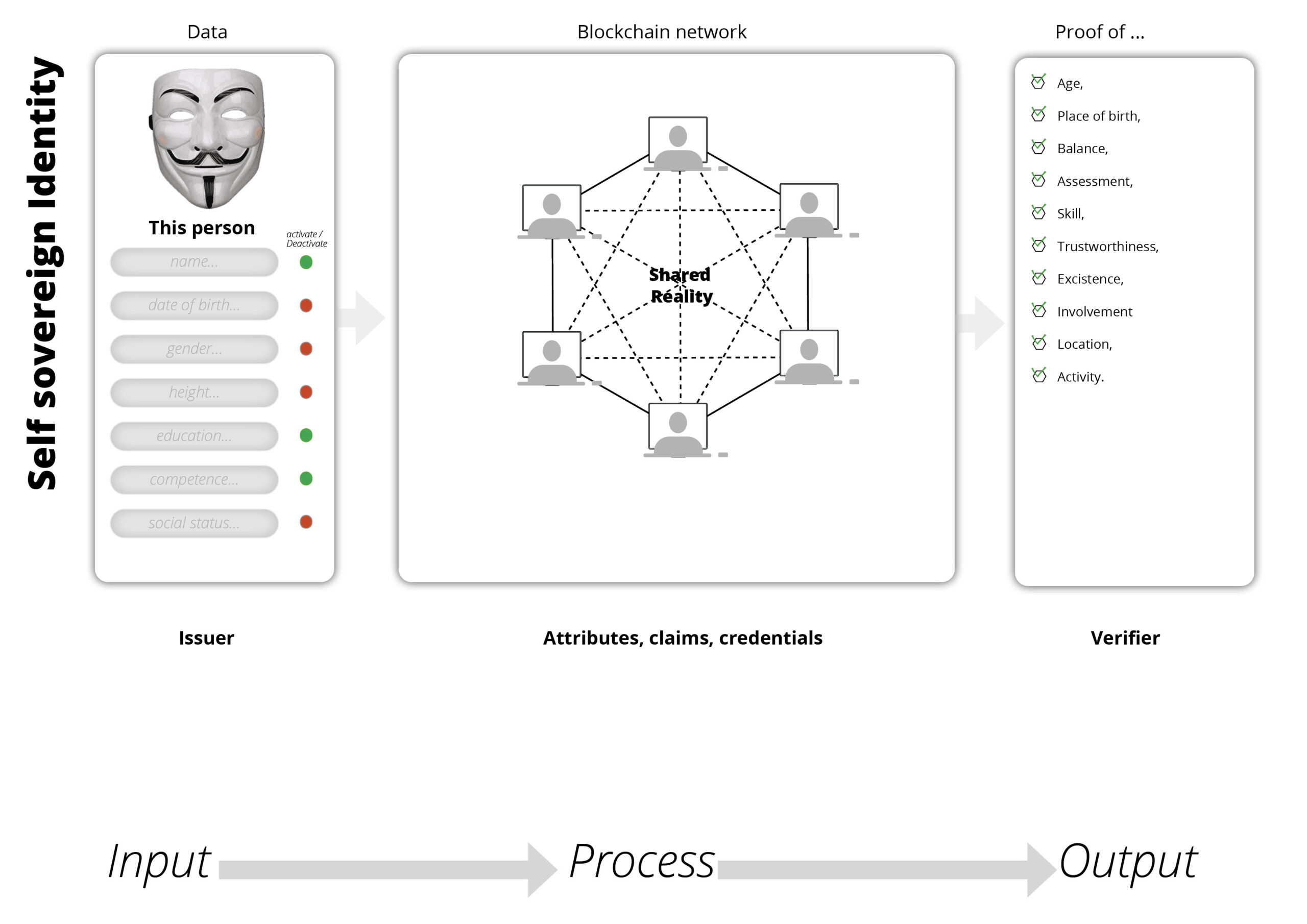
Unique identifiers for people (SSI), companies (wallets), for content (CID) and products (DID’s). DID’s rely on cryptography to prove that you are in control of a given identity.
Relationships
Digital data carriers on physical products (like a QR code, RFC) with look-up mechanism. Legal identity identifier (LEI).
Rules
Data processing, data exchange, storage, authentification, integrity, security and privacy protocols
Resources
Intellectual property, verifiable credentials, linked Data links information to a precise uniform Resource identifier (URI). Similar as URL points to a specific website, a computer can automatically understand the information received from a URI.
Result
Digital identities, verifiable Credentials and Linked data are powerful examples of standardization. It makes it easier to analyse and improve the whole. For example: ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation, GHG emissions reporting.
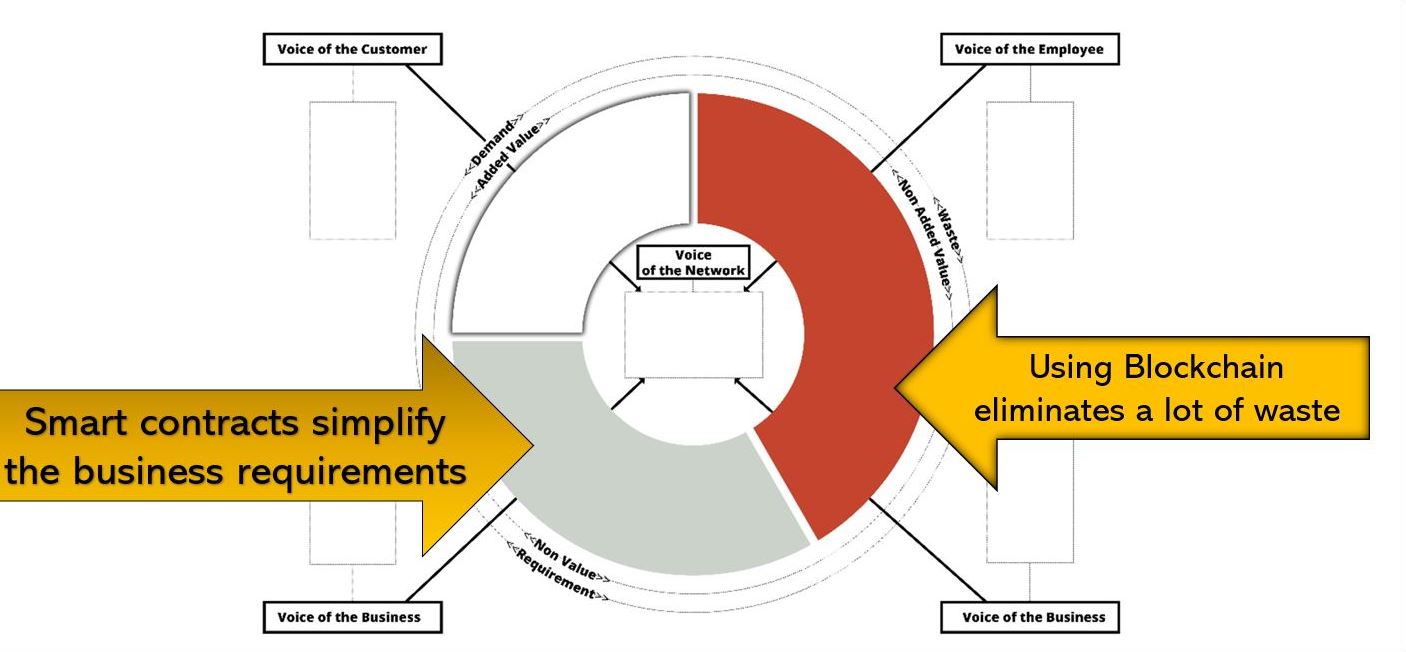
Value stream mapping – reinventing value flows
Value stream mapping
Provides a visual representation of the value and non value adding activities. It is used to optimise and understand a process.
- Value adding (VA)
Activities the customer is willing to pay for. - Non value added (NVA-W), waste
Peer-to-peer transactions eliminate numerous constraints in the flow of value, such as waiting times, overproduction, overprocessing, defects, and the need for intermediaries. By removing these non-value adding activities, blockchain streamlines the value exchange process, making it more efficient and seamless. - Non value added (NVA-R), requirements.
Smart contracts revolutionize collaborations by enhancing their efficiency, effectiveness, and predictability. These intelligent contracts establish the new rules of the game, providing a reliable and automated framework for conducting business transactions. With smart contracts, parties involved in a transaction can trust that the agreed-upon terms will be executed accurately and without the need for intermediaries.
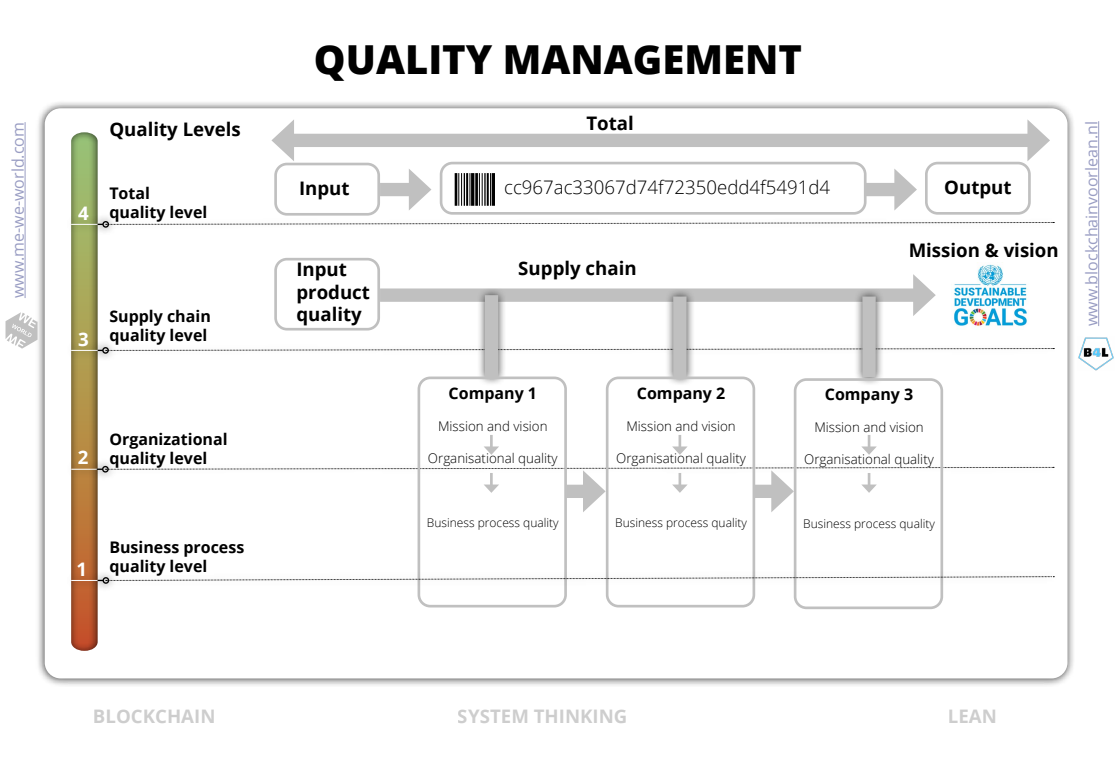
Quality management
How does Blockchain improve quality management?
Product
Blockchain brings transparency to the input quality. It makes it possible to verify and prove authenticity based on Smart data. It is even possible to tokenize real assets by creating a digital twin and track and trace the unique item throughout the entire supply chain. Also documents, qualifications, licenses, certificates can be digitized.
Organizational
The purpose (Hoshin Kanri) of a blockchain is based on a shared understanding (standards) and reality (visualization). A lot of waste is avoided by the re-use of data from the source (waste/trust management). With signals (kanban) and direct feedbackloops (alignments) it looks like a supermarket model (Taiichi Ohno).
Business
With blockchain the Who, When, What becomes clear for the entire process. It brings consensus to the needs, the expectations and critical activities of all participants. The end-consumer is often part of the solutions. This makes it easier to measure and monitor satisfaction and take appropriate actions to improve the functioning of the entire chain.
Total Output Quality
By collecting information about the possible environmental, social and economical costs and benefits or advantages environmental full cost accounting becomes reality.
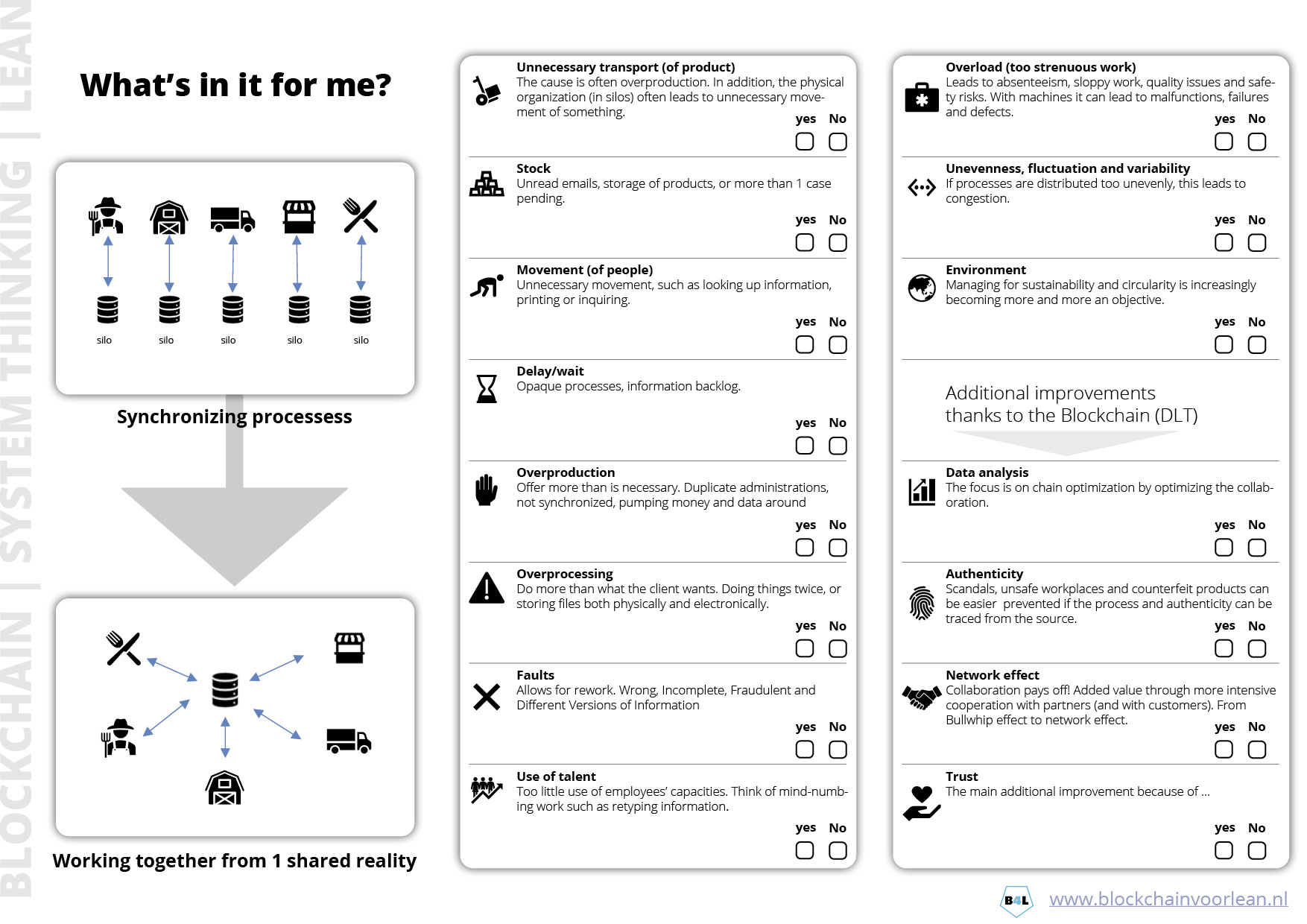
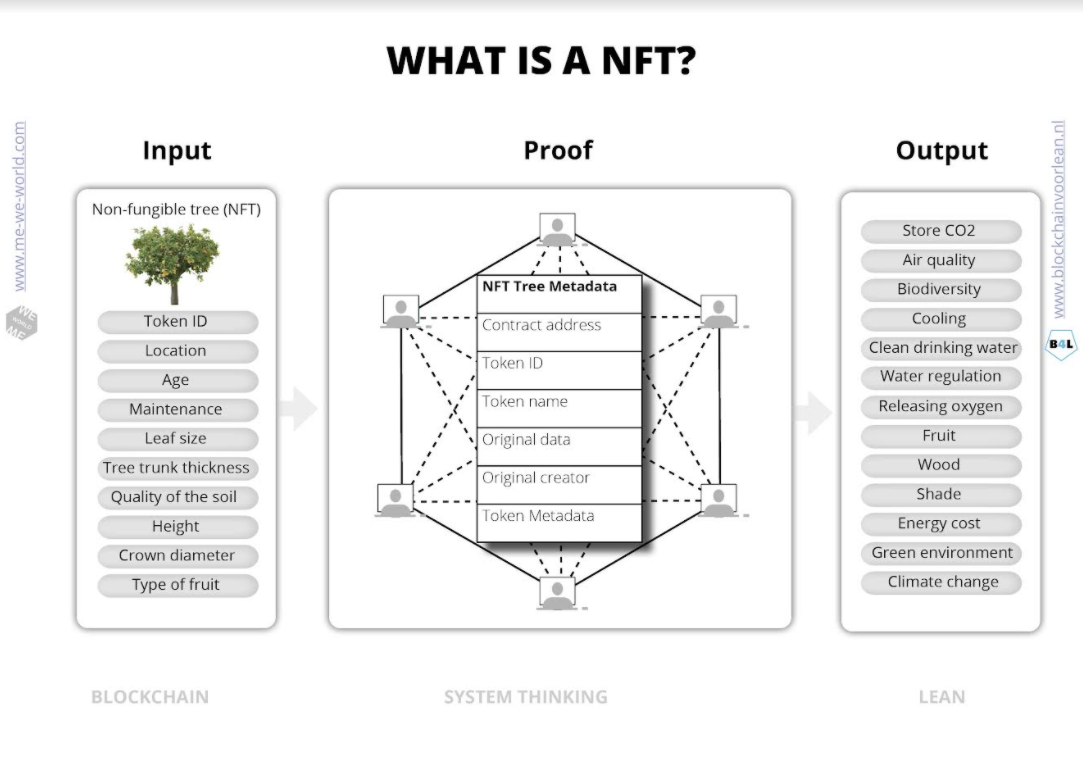
What’s in it for me?
What is a NF Tree?
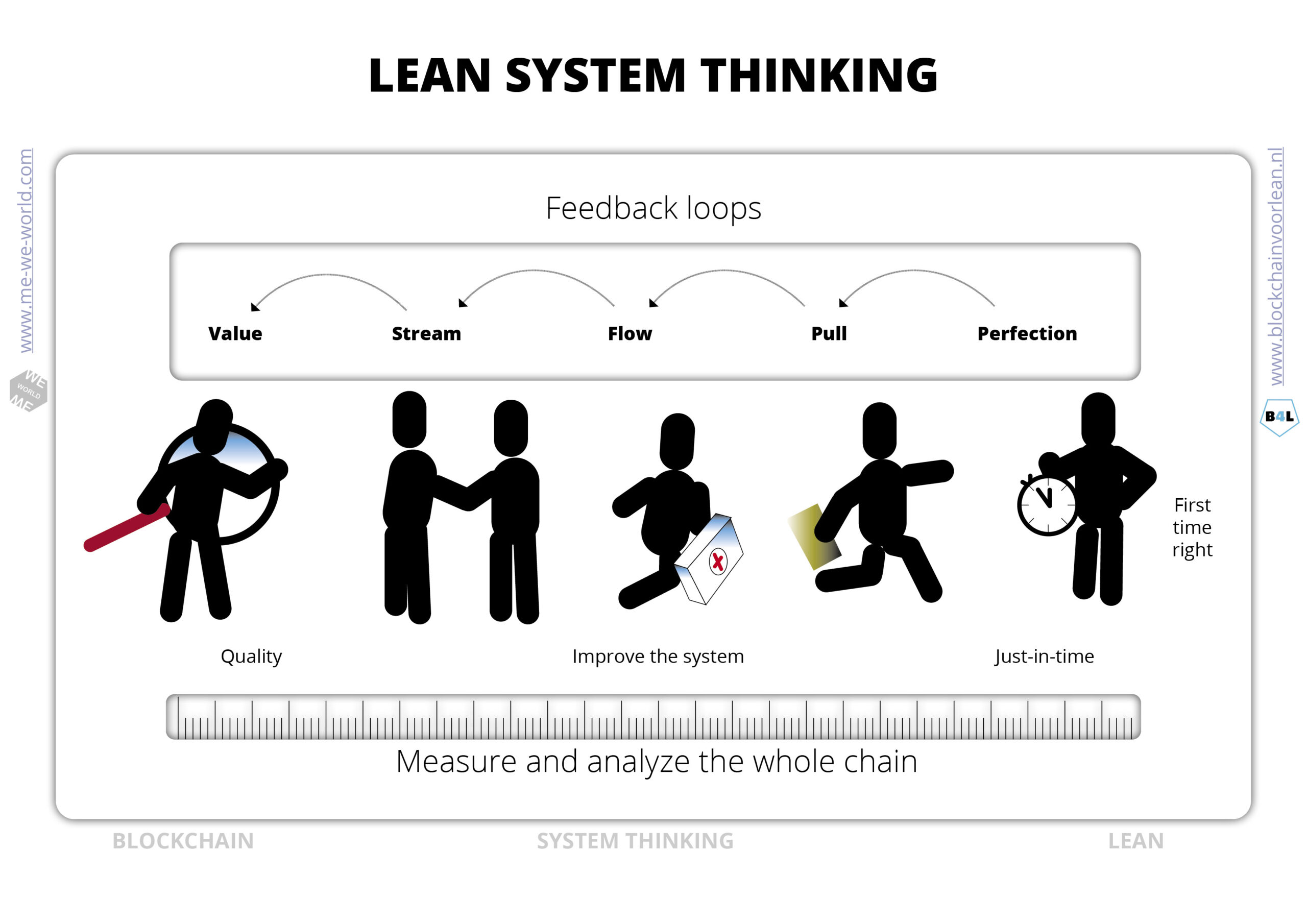
Lean thinking – Lean system thinking
How do you create alignment with focus on quality management?
- Customer focus
- Network governance/collaboration
- Incentives/alignment for value adding activities
- End-to-end process approach
- Network improvements,
- Feedbackloops
- Evidence-based desicion making
- Agility, system thinking, respond to change
With Lean a status overview is often used to provide insight of information, like who, what and when things where done. Blockchain provides in a transactional and status overview to do this for end-to-end processes. The status is updated when a transaction takes place in the network and it gives certainty of ownership and execution with the approval of all stakeholders. We now have a collaboration (lego) toolset to improve the quality, reliability, flexibility, cost and throughput of interactions between businesses. Thanks to the direct feedback loops from all the coalition partners/stakeholders, the system can be continuously improved.
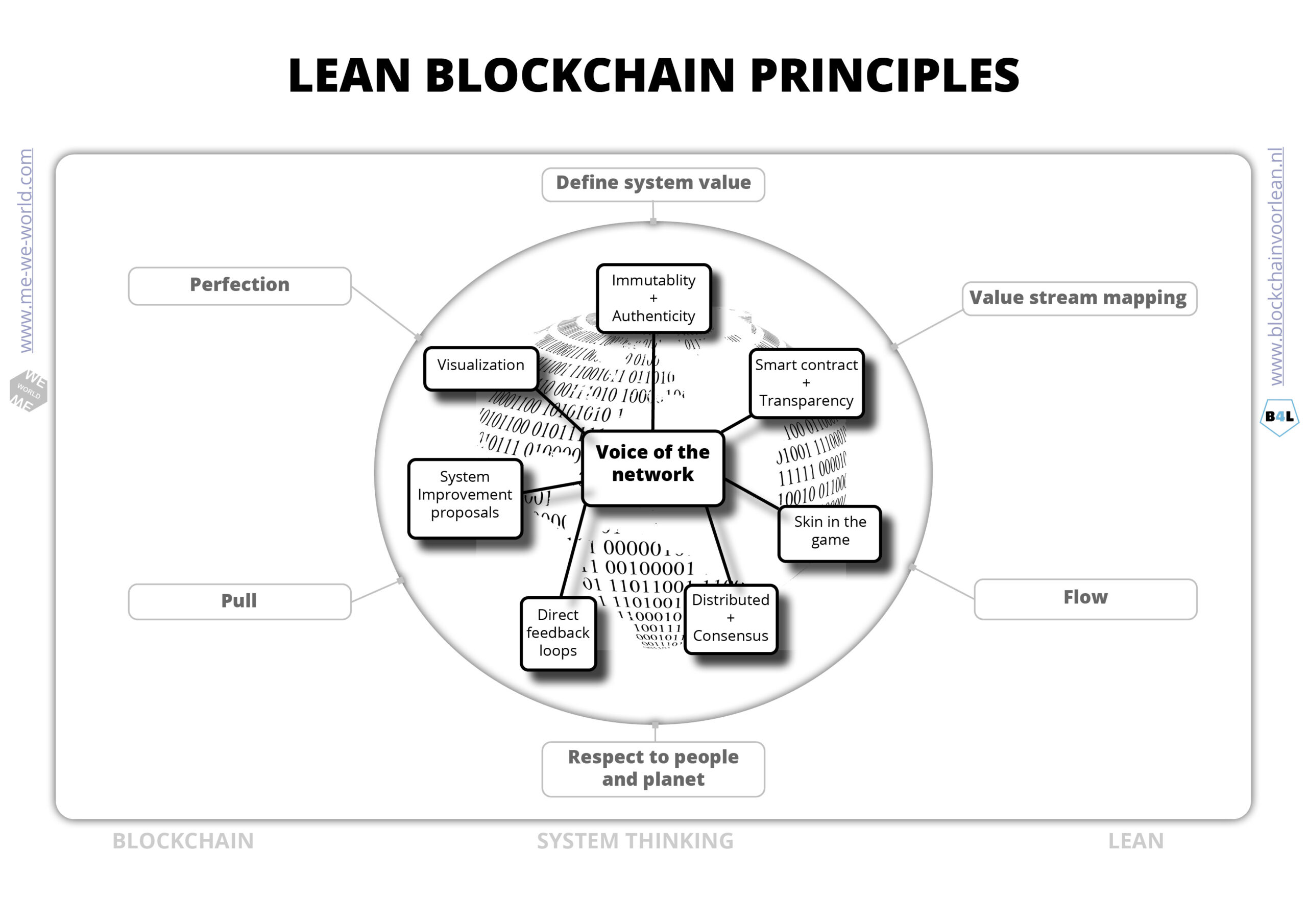
Lean Blockchain principles
The power of a blockchain is to solve multiple problems at the same time with a shared mission and vision. The economic functioning of a blockchain system is called tokenomics. It describes the governance, incentives and economic design. It focusses on the behavior and interactions of participants in the system.
Important to analyze and clarify:
• arrangements
• expectations
• roles
• contributions
• incentives
• assumptions.
Blockchain for lean is a business strategy based on lean thinking, lean system thinking and improving flow with better alignment, collaboration, incentives and co-creation. Be part of the lean-blockchain coalition and find the others!
A Voice of the network analysis helps to determine the interests and goals of each participant of the network. It gives directions how to find common ground, shared interests and fair incentives to contribute to shared goals. This is important because different stakeholders have different needs, purposes and goals. “Meeting customer expectations” and designing contributions and incentives to shared goal, are the main drivers for a successful Lean or blockchain project.
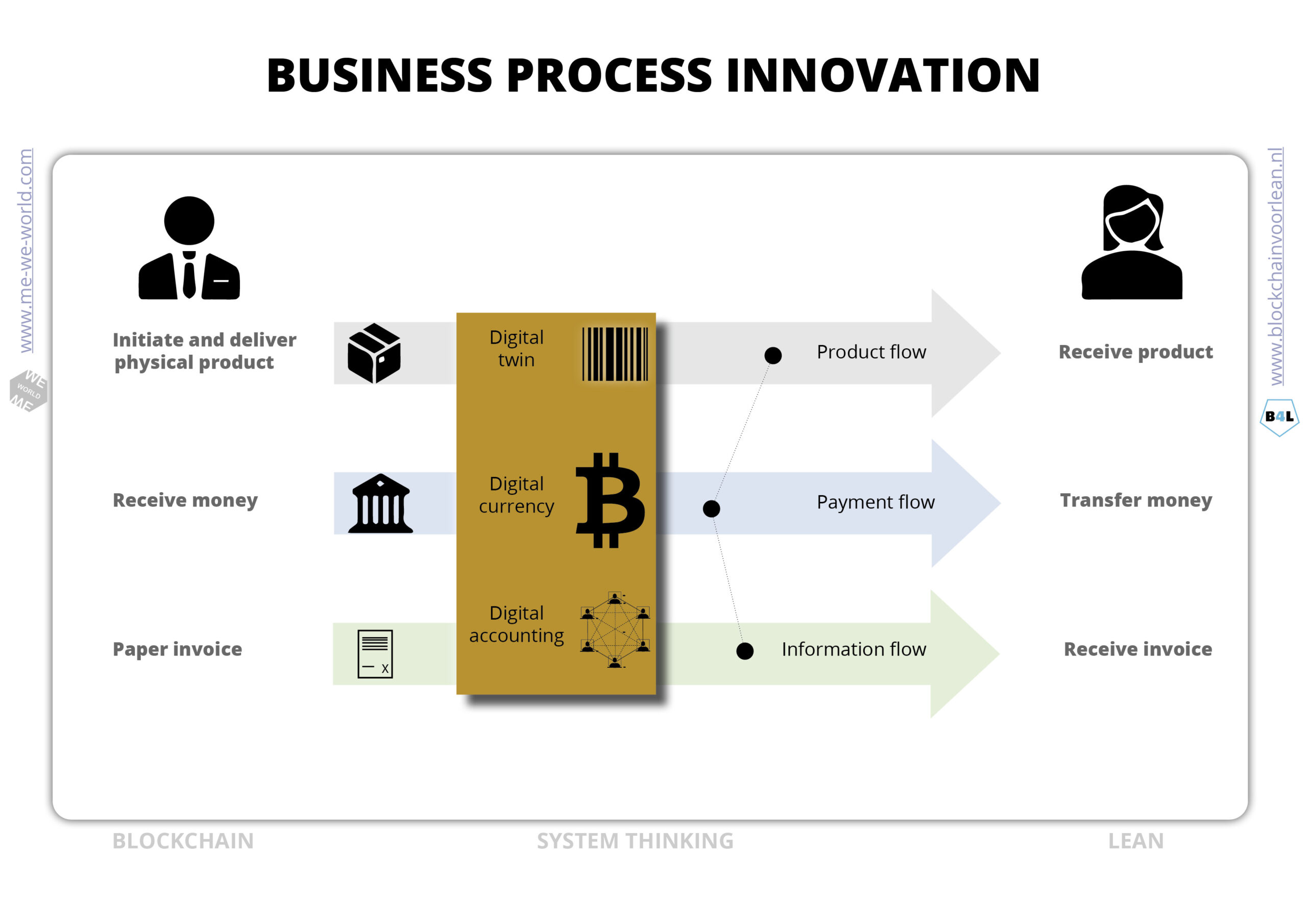
Business process innovation
In processes the material flow (what is needed for production) is often decoupled from the information flow (information what needs to be done) and payment flow. Decoupling of flows causes waste in operation, such as unnecessary stock, loss of quality, waiting, over processing and so on. Synchronizing these 3 value flows is called “settlement”.
By digitizing the product, payment and information flow these flows can transact simultaneously in an one piece flow (transaction). The goal is to reduce settlement time to zero.
Note that the decoupling or fragmentation of information (value flows) leads to further coordination issues, like waiting, emailing, inquiry, research, control, overproduction, trust issues etc.
With linked, digitized and tokenized (atributes/passports) of data, settlement can be synchronized and available 24/7. By optimizing the transfer of value flows and thinking in systems a lot of waste is avoided.
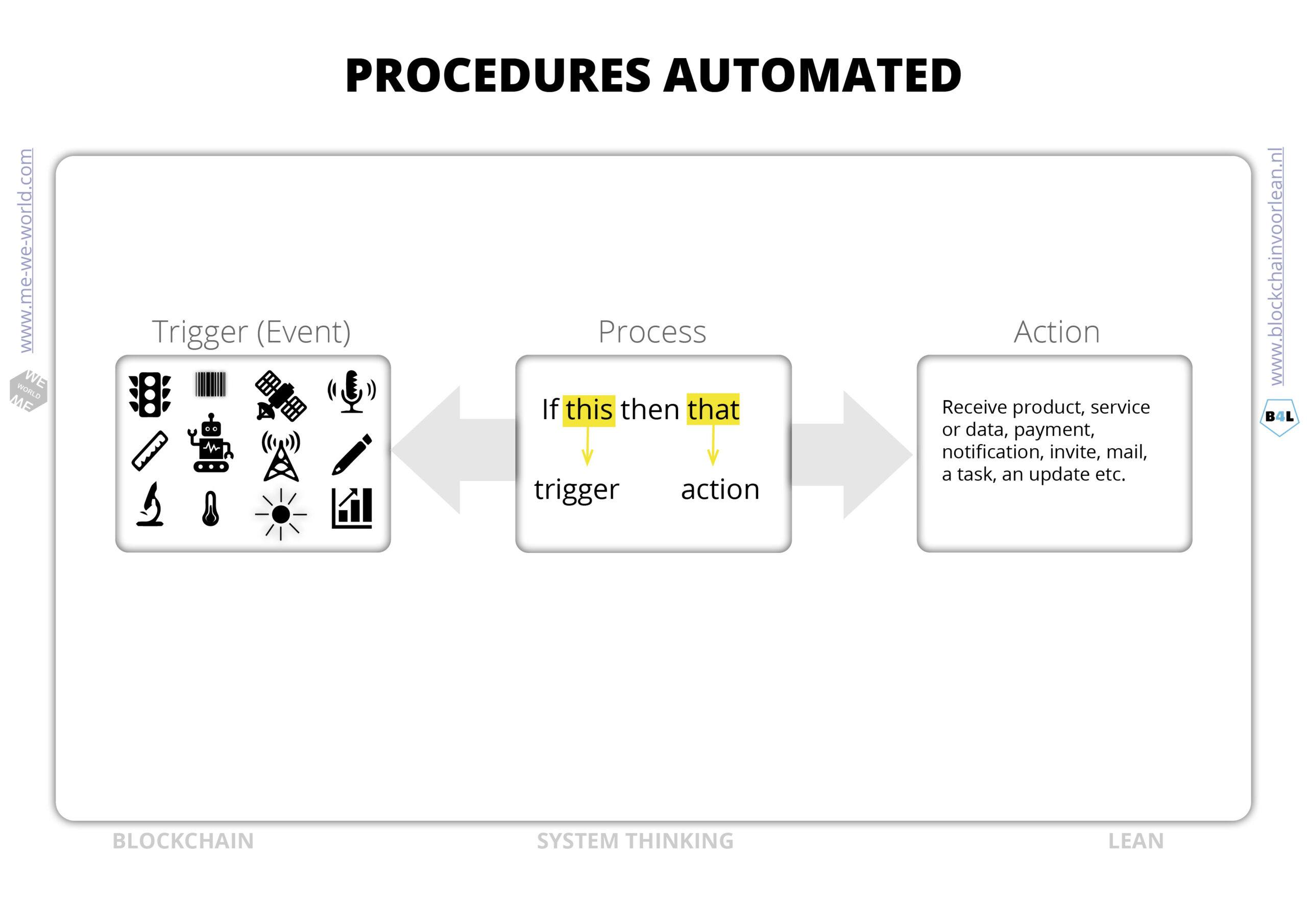
Procedures (SOP) automated
Human collaboration is underpinned by relations, contracts and procedures. A standard operating procedure (SOP) is a written work instruction that describes in detail how a certain action should be performed. Blockchain and smart contracts in combination with “oracles” brings new ways of executing contracts and procedures on the internet. They differ in the way they execute digital agreements (automated and distributed) and also the way data is recorded and stored is different. Data flows from the source, becomes immutable (delete button is missing) and actions are done with consensus beforehand.
Performance data will trigger the contract. The data can be generated online or offline. Validation and verification of the data is an important part of the system design: garbage in = garbage out.
Anyone can agree on a binding agreement on the internet. The smart contract offers participants a guarantee that the contract will indeed be fulfilled when an event occurs.
A participant does not have to trust any another participant. The contract will be executed when an event has taken place. Trust is integrated in the system (code). This makes end-to-end processes more reliable and predictable.
Start with why?
If you have any doubts on the potential of blockchain, then ask yourself the following questions:
- Why do we all keep our own records? While we know that this is one of the biggest bottlenecks for value flow.
- How do intermediaries contribute to value flows? With limited opening hours and centralized power.
- What problems can be solved with adding more transparency?
- What makes it so hard to settle process, product and payment flows?
- How can we ensure sustainable cooperation, better coordination and communication?
The internet changed the way information flows. Today, we’re implementing and redesigning the way value flows.
For a big part blockchain technology is about redefining processes and forming the coalition of the willing. For this it is important that changemanagers inform and inspire people with the new possibilities.
Lean thinking and lean system thinking is the basis. The biggest challenge isn’t the technology, it is changemanagement from a more hollistic/system approach!
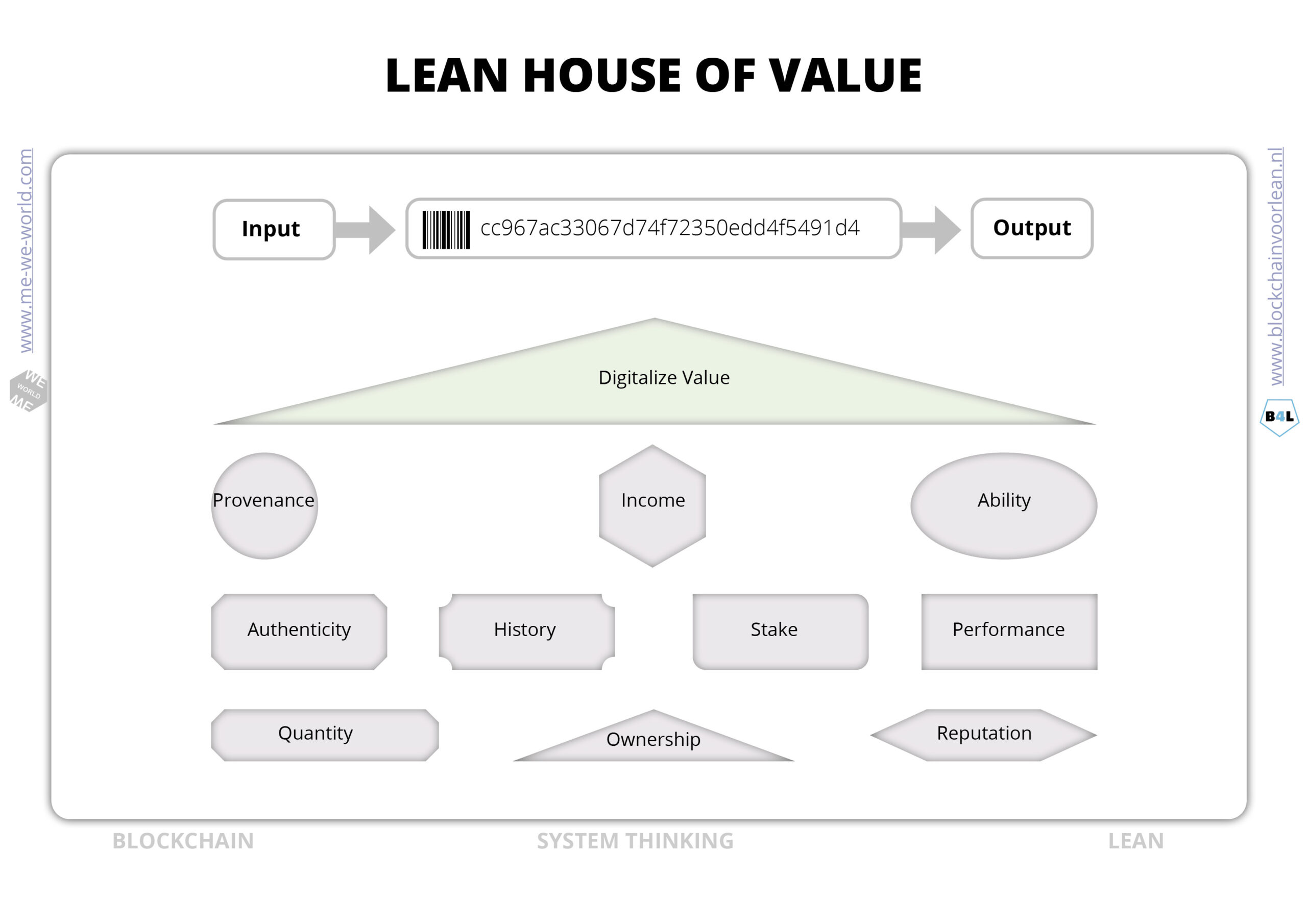
House of Value
Every process has a specific purpose. The goal of the process determines what is of value to the customer. Values can be translated into concrete standards with concrete taxonomy and regulations, but also in more intangible aspects like customer satisfaction or desired behavior. With blockchain and smart contracts it becomes possible to reward people for desired behavior, reach consensus and contribute to the purpose of the community. So what is value?
Tangible assets
Tangible assets are assets with monetary value in a physical form. It is worth a specific amount of monetary value and can be traded.
Intangible assets
Blockchain technology is a time stamping tool which makes it possible to register every interaction on the internet. Also intangible assets can be registered and rewarded. Think of liking or sharing content, reading or editing articles, or receiving a package for the neighbor. But also a company’s reputation, copyrights, trademarks, brand recognition can be digitized and transferred. This makes blockchain a new incentive mechanism for motivating people to do certain tasks.
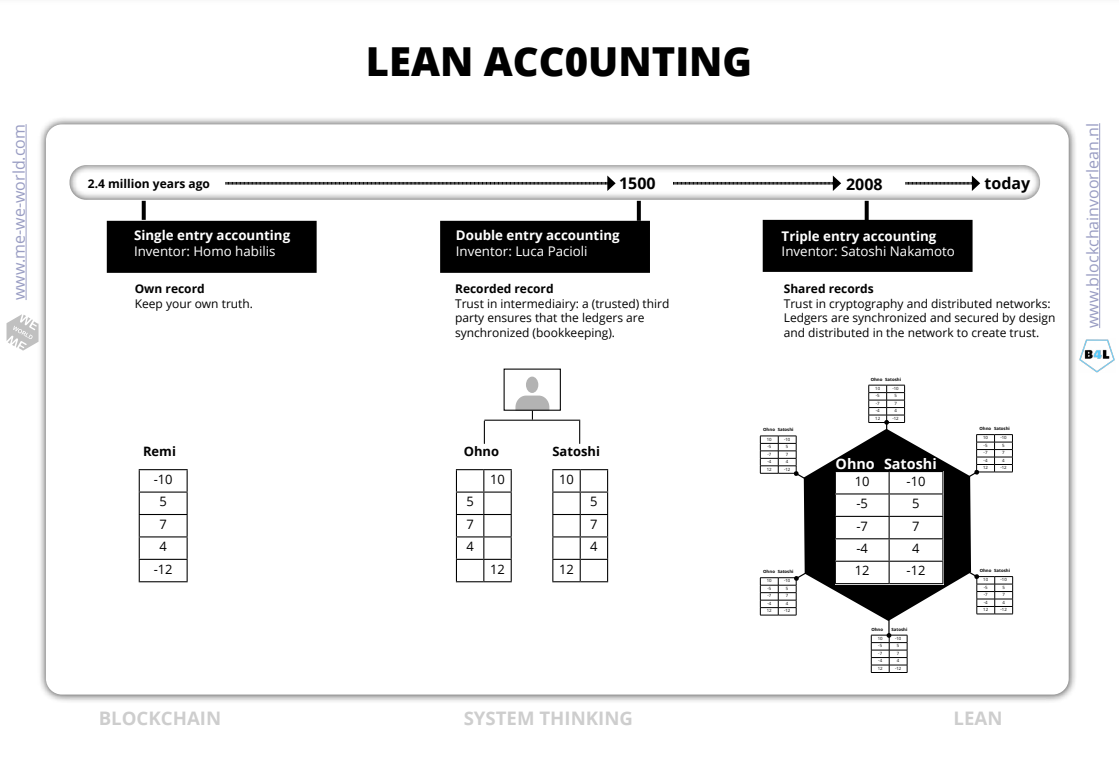
Evolution of accounting
In daily live we do a lot of transactions. In fact, you could think of any interaction as a transaction. However, we only record valuable transactions by writing them down in ledgers/ databases/registers. Those ledgers allow people to demonstrate his or her property or achievements to gain value in a social context. Basically they coordinate ownership, identity, the status and authorizations.
Central coordination: proof by authority
So everything that has value is nowadays stored in ledgers. Those ledgers are the starting point for all transactions of value. Organizations that provide storage and access to the data are called intermediaries or third parties. Intermediaries exist because we don’t trust each other. Intermediaries therefore organize trust and play a pivotal role in this. And the customer pays for this service.
Trust in cryptography
Blockchain technology solved the “double spending problem” on the internet. For the first time in history peer-to-peer transactions can be executed without the need of an intermediary or third party.
The technology is often called “digital ledger technology”. By timestamping balances and providing access to those balances it can (partly) replace the work of the intermediary.
Suppose we no longer use an intermediary for transactions of value on the internet? What will happen to the processing time, the quality and the cost of those transactions? And of course the customer value?
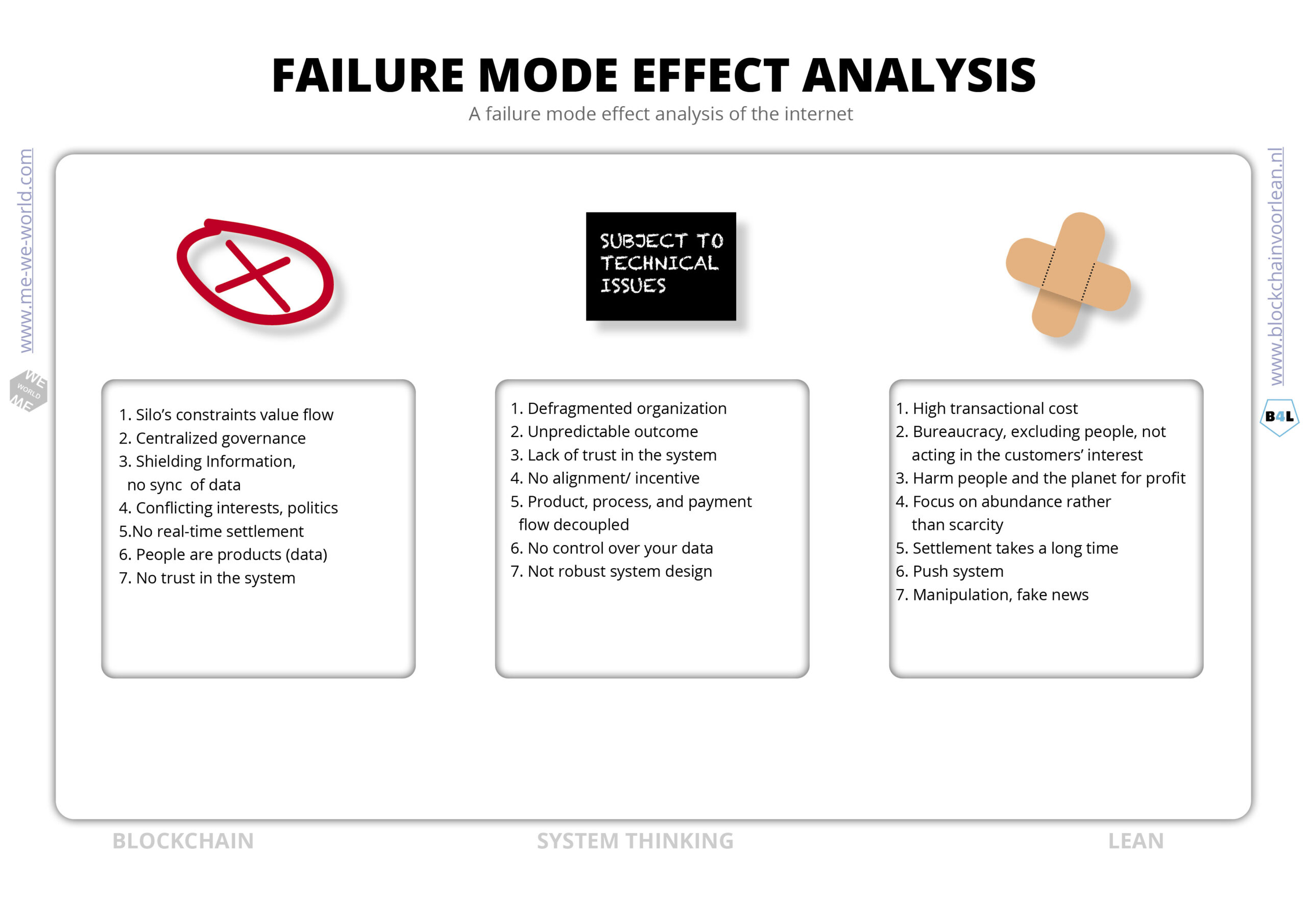
Failure Mode Effect Analysis
The best way to avoid mistakes in processes is to design a fool-proof system. What if we design a FMEA for the internet? An Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) examines which disturbance can occur in processes and analysis the causes and the effect. How would such an analysis look like for business 2 business processes? And how could blockchain solve those issues?
The idea of a blockchain is that stakeholders share information with other stakeholders to improve the collaboration, communication and coordination. The goal is to align and balance value adding activities to the purpose and goals of the network/coalition.
The system design makes sure that every transaction contributes to the common goals. By digitizing the product, process and payment flow the operational (settlement) and maintenance cost can be significantly lower. Also the scalability and accessibility of real-time information leads to a more efficient and effectiveness workflow. The owner of the data is no longer a “product”. With blockchain the owner “signs” and approves transactions and decides the availability for every other (authorized) stakeholder.
Do need a Blockchain?
There are various decision trees to determine whether blockchain is a good idea. If 4 of the 5 of the decision rules below can be answered with ‘yes’, there is a good change blockchain will have added value.
- Lack of trust. Suppose you don’t depend on a third party to find out that something is true.
- Lack of alignment and collaboration. Are you working with businesses that you don’t trust and with different interest and goals?
- Temper proof. Do you want to be dependent on someone you cannot trust.
- Automatic execution. Is the verifiable execution of processes (business logic) important
- Lack of flow. Will the throughput/lead time improve by sharing (re -use) information from the source? Will it prevent from waste? Like e-mail?
For business to consumer processes we find it quite normal that we have a track and trace system to follow transactions (the status) of an order. How is this completely different for tracking an tracing an status through a business to business network! Or for solving a worldwide Covid19 crisis. You can’t solve these big problems inside your business walls or inside your country borders.. We are interconnected. The world has a coordination, cooperation and communication problem! We need to collaborate, set a shared mission and vision and be transparant over the goals to be achieved.
Even a good person can’t beat a bad organized system. Let’s reinvent who value should flow!
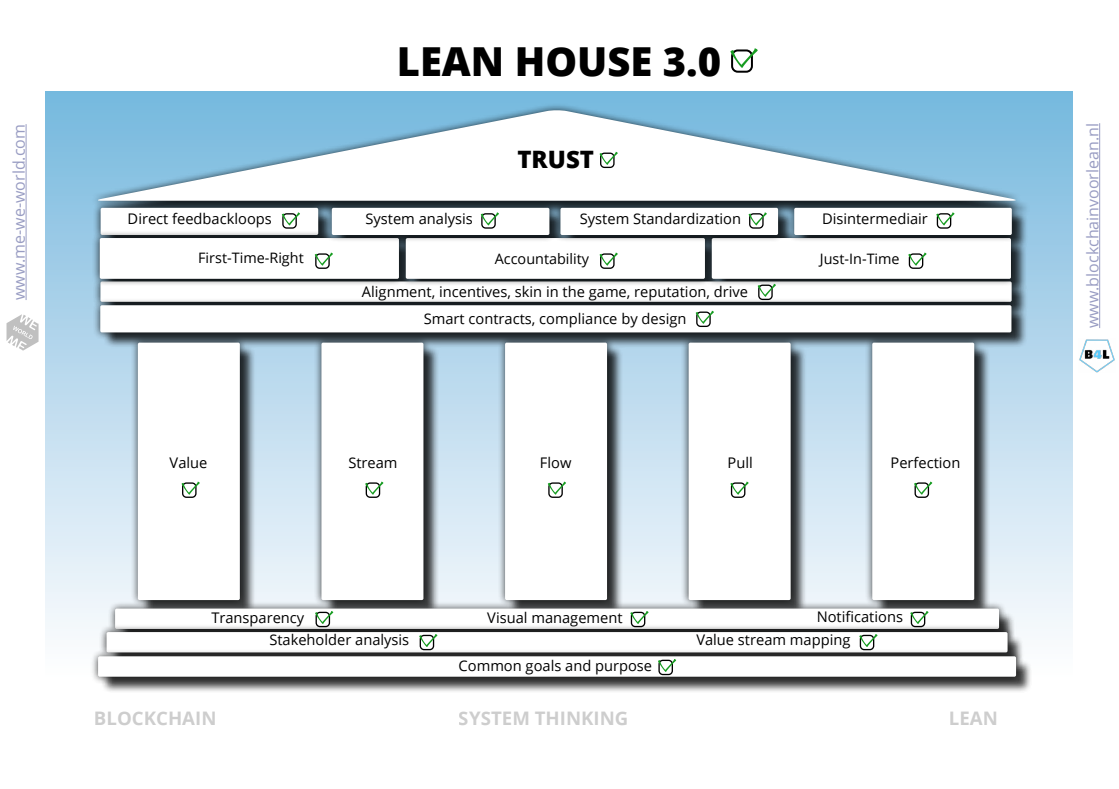
lean house
What are the 5 key elements that blockchain adds to the lean house?
1. Alignment of Purpose
Processes are a derivative of an organizational strategy and determine the common goals and shared values. It gives “purpose” to the organization and enables alignment with people and processes. BC enables this for business collaborations.
2. Build in trust
BC has solved the double spending problem on the internet. Processes can be redesigned without the need of a (non value adding) trusted third party in the middle.
3. Value Stream
How do you get flow in processes if the value flow is continuously interrupted by an intermediary? BC allows value to pass from hand to hand. Transparency and visual management provides insight and control by design for all participants.
4. Quality and time
Blockchain shares information from the source/expert/oracle. This method not only saves a lot of time (just-in-time) and costs (first-time-right), but also ensures that the input quality comes from the expert.
5. Culture
What if we could design an infrastructure that contributes to the 17 Sustainable Development Goals? We now have the tools (BC, IoT, AI) and knowledge (lean thinking).
Lean system thinking
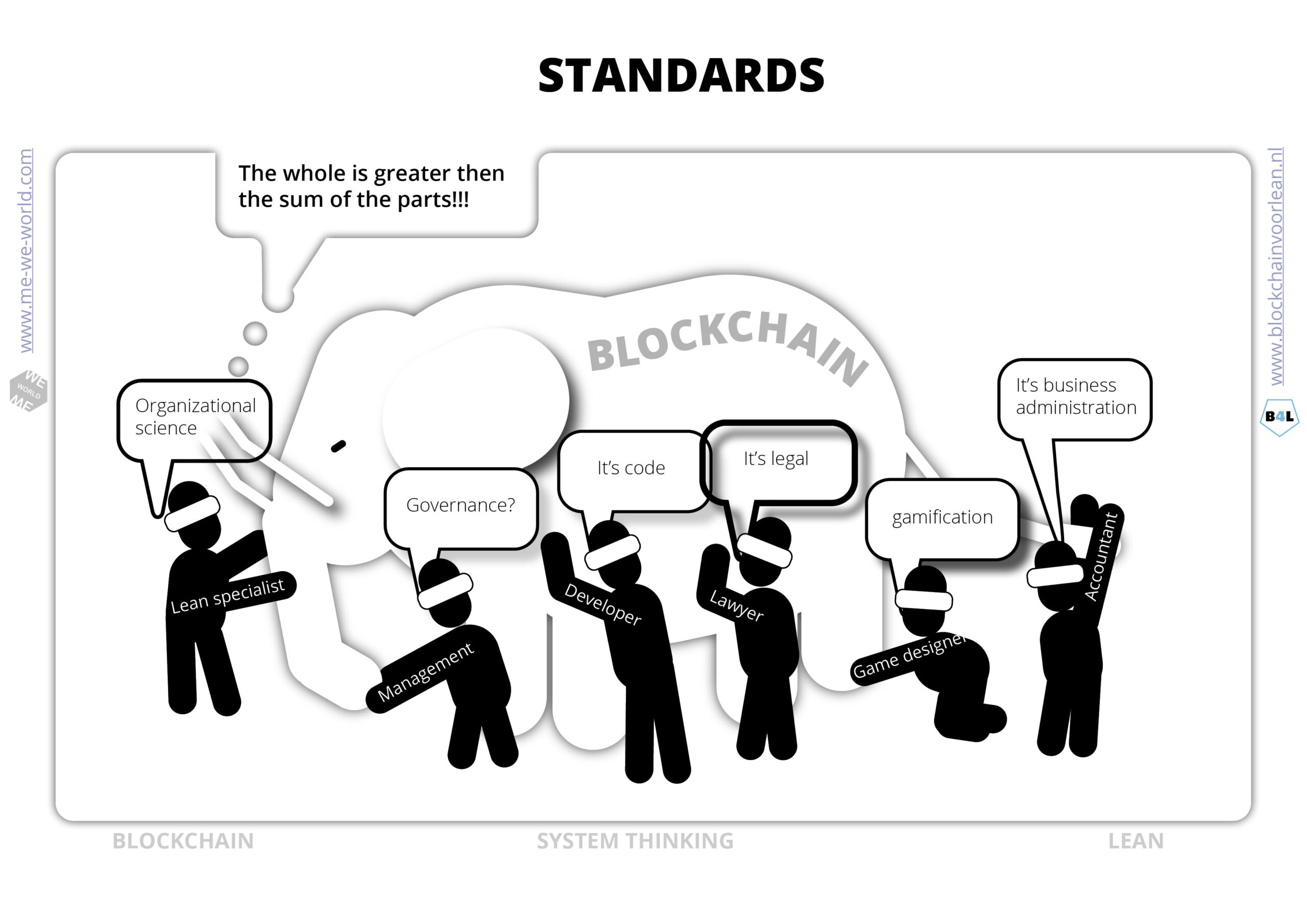
Have you ever heard of the “Nine Blind Men describing and explaining Blockchain technology”?
With Blockchain for lean we focus on the changemanagement perspective of the solution. The technology brings new opportunities to eliminate waste in processes. That’s why we call blockchain a lean system thinking method. The technology is useful if you want to solve problems that you can’t solve within your own company walls.
With blockchain for lean we are happy to inform and inspire changemanagers, CEO’s, lean consultants with different kind of “lean system thinking” usescases. You will learn to improve the input quality, the throughput and output by smarter collaboration, coordination and communication.
Know that Blockchain is an ecosystem and not a plug and play solution. This makes it hard to understand and explain. But don’t be discouraged. There is a lot of information available. Just ask for it. In an ecosystem there is a place for everyone!
Lean Blockchain principles digitized
Blockchain goes beyond the elimination of waste. Let’s talk about the lean principles from a Blockchain approach.
- Define network value
In traditional supply chains companies pursue their own values and goals. Blockchain is a coordination, cooperation and communication toolkit that aligns value created by the network. It brings clarity to the purpose of the whole chain and brings standardization of value adding activities of the end-to-end processes.
- Value stream and flow
Oracles or digital twins are used to determine the input data quality. They play the most important role, because if you can’t trust the input quality, the whole setup is worthless.
The value becomes digitized (digital twin) and stored in a immutable token. Thereby a token is a representation of network value.
- Pull system
The token can be transferred peer-to-peer (from wallet to wallet). There is no need for a third party as everyone has access to a copy of the current status.
- Perfection
Lean stands for understanding what is important to the customer. With Blockchain there is no one customer. Every stakeholder benefits from bringing improvements to the input quality, the throughput and the end result. It’s a system of lean collaboration with shared interest and goals.

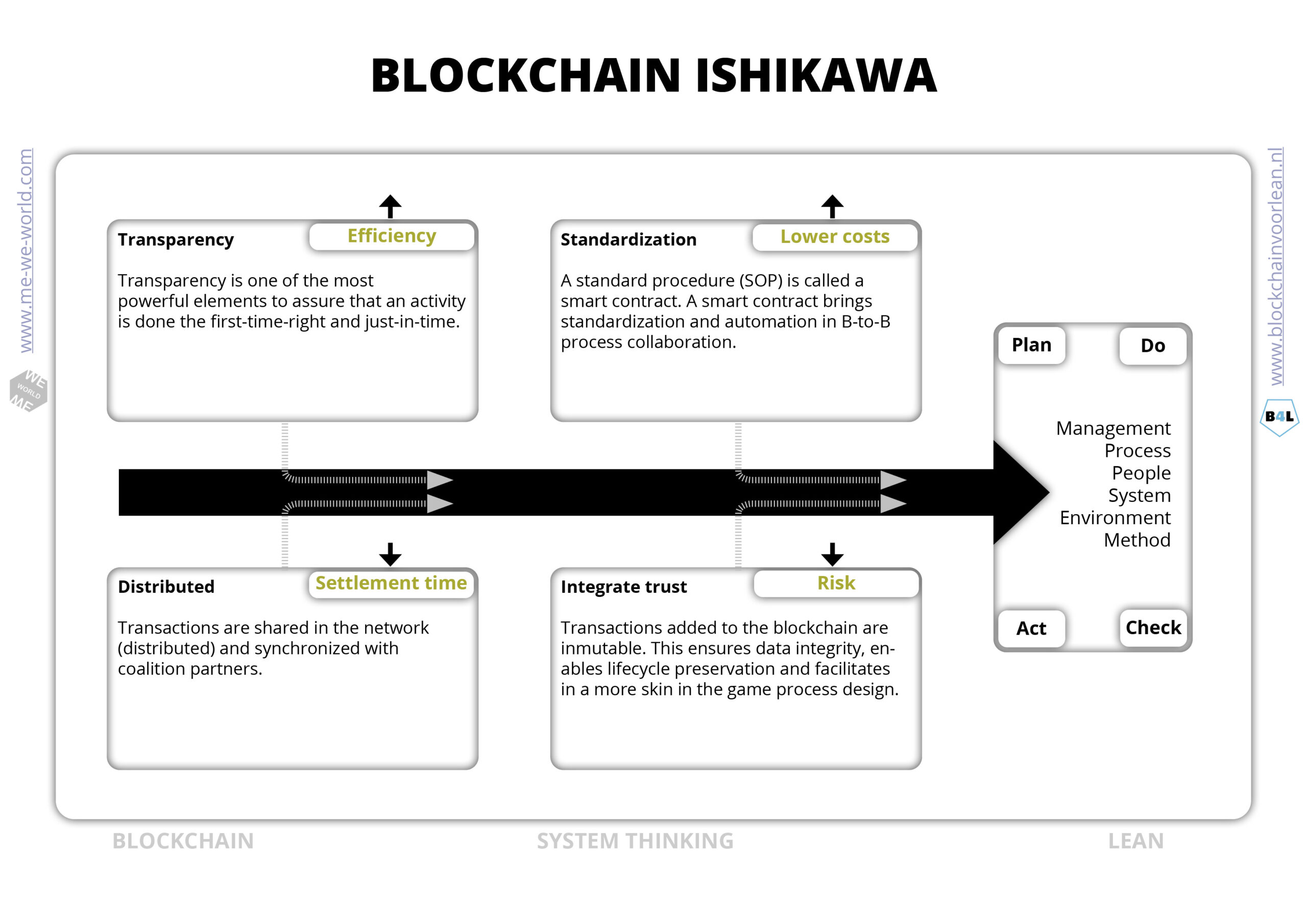
Ishikawa – a lean conversation starter
The Ishikawa diagram is a tool intended to map possible root causes of problems. Can it also provide insight into the main benefits of a blockchain solution? Why is lean system thinking helpful?
As Einstein puts it beautifully: “we cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them.
Start thinking of optimizing end-to-end processes. Then businesses have to collaborate on common goals, assure alignment and be able to trust each other.
The concept of a blockchain can be used as a “Lean conversation starter” for creating insight, cohesion and shared understanding. With the help of a Ishikawa diagram in combination with a lean blockchain validator we can “proof” the benefits for each stakeholder.
Lean innovation – Digitize value flows
“What the internet did for communications, I think blockchain will do for trusted transactions.” is a famous quote by Ginni Rometty (CEO IBM).
With blockchain technology the process, product and payment flow can be digitized. This makes track and trace applications possible for B2B supply chain solutions. With integrated alignment and direct feedback loops the collaboration can be continuously improved.
A blockchain is a digital ledger that can be used as a status overview in a network of transactions (interactions). Traditionally a ledger is used to provide in a statement of account for a business. For example the financial position; ownership of assets, equity or liabilities. Or the statement of account of income and expenses.
With Lean a status overview is often used to provide insight of information, like who, what and when things where done. Blockchain provides in a transactional and status overview. It is updated when a transaction takes place in the network and gives certainty of ownership and execution with the approval of all stakeholders. We now have a collaboration (lego) toolset to improve the quality, reliability, flexibility, cost and throughput of interactions between businesses. Thanks to the direct feedback loops from stakeholders, the system can be continuously improved.

Medium of exchange
In our daily life we do a lot of transactions. In fact, you could think of every interaction as a transaction. However, we only record valuable transactions. Transactions that have value have been recorded and maintained in ledgers and managed by organizations/institutions for many years.
What is a valuable (transaction)?
This is hard to define. Besides art-work, money etc, also attention, like-en, swipe-en and access to data can be considered valuable.
How do we call these organizations that store and give access to our data? Third Parties or Intermediaries.
Why are ledgers important?
In ledgers we store ownership. This is important to gain value in a social context and the starting point for valuable interactions.
Why do intermediaries excist?
Intermediaries exist because we don’t trust each other. So, there function is to organize trust.
Is there also an other possibility to do so?
Good point! The usecase of blockchain is to digitize ledgers and to maximize customer value while minimizing waste.. Or is this lean thinking?
The internet started with sending an e-mail to transfer information. Blockchain is started with installling a crypto wallet on your computer to make value flow. Are you already there?
Blockchain: lean principles and tools
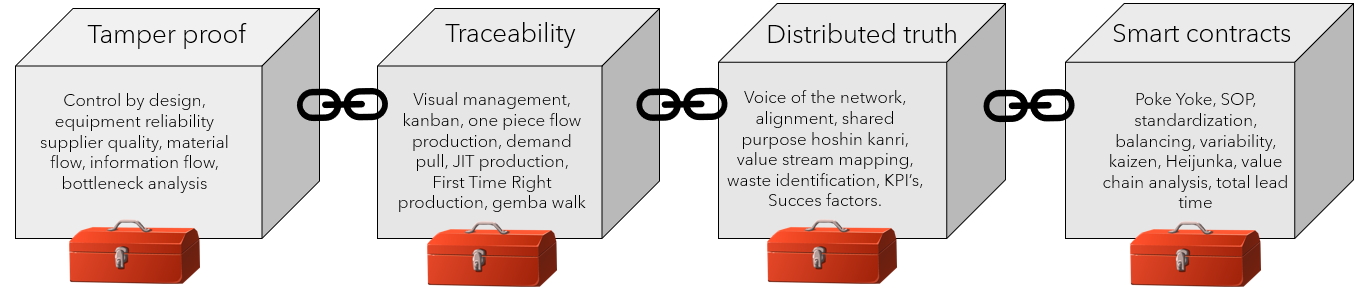
Blockchain is not always well understood. This while the concept of a blockchain incorporates a lot of lean principles and tools. The main difference is that the principles and tools integrated in a blockchain are not used to optimize your own business processes, but optimizes the interaction between different stakeholders (over business walls). If you look beyond the bits and bytes you will see why blockchain is such a powerfull lean tool. In the picture below we pointed out 4 blockchain features including the lean advantages.
- If processes are recorded immutably ownership and responsibility will be automatically part of the system design. Keeping history makes it also easier to address external consequences.
- Tracking data from the source ensures data integrity and reduces the need of checks afterwards. The transactional design is made in such a way that the transactions are done the first-time-right and just-in-time.
- A shared reality removes all non value adding activities. It prevents from disputes and rework and integrates direct feedback loops. The collaboration, cooperation and communication can be improved continuously.
- Accelerate error-proof execution by automating standard operating procedures. This makes it possible to measure, analyze and balance the performance of the system. The critical succes factors heavily depend on the intensity of cooperation.
Lean Kaizen, Kaikaku en Kakushin
Wat is het verschil tussen Kaizen, Kaikaku en Kakushin?
- Kaizen is een methodiek om mensen te leren verspillingen te gaan zien en deze te elimineren. Het streeft naar een cultuur van continu verbeteren.
- Kaikaku wordt ook wel breakthrough Kaizen genoemd. Het brengt een revolutionaire verandering in de traditionele werkwijze. Denk aan een digitale transformatie.
- Kakushin richt zich op innovatie, hervorming en vernieuwing. Waar Kaikaku zorgt voor transformationele verandering van bestaande structuren en systemen, introduceert Kakushin volledig nieuwe structuren, systemen, aansporings -en verdienmodellen enz.
De impact van een nieuwe technologie is vooraf vaak moeilijk in te schatten, maar achteraf zo logisch. Blockchain technologie is een nieuw samenwerkingsconcept. Doordat er gewerkt wordt vanuit een gedeelde informatiebron worden de kosten van afstemming aanzienlijk verlaagd. Dit klinkt niet alleen logisch, vinden wij, maar is ook heel lean!

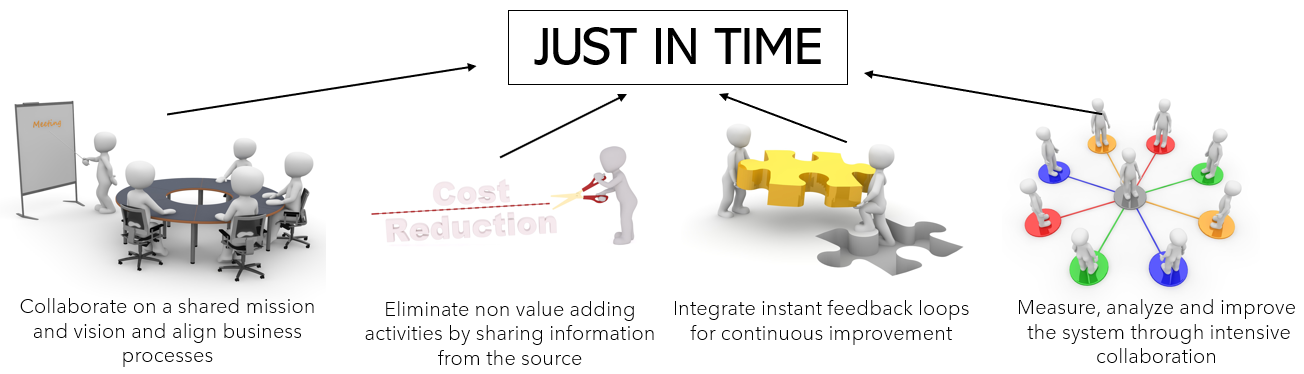
Just-in-Time
Just in time means delivering exactly what the customer needs; the right product, in the right quantity, at the right time. The aim of the methodology is to optimize coordination between the logistics of stakeholders and create maximum flow and minimize internal stock. Blockchain will integrate process and product information within and across enterprise boundaries. What ERP (Enterprise resource planning) did for a single company blockchain will do for networks of companies.
System thinking
With design thinking the goal is to think in a cooperative system to overcome traditional bottlenecks in value flow. Lean consultants already know that transparency, standardization and real-time information are very powerful tools to reduce variability and instability in a system. With blockchain these tools are integrated in the concept. An additional benefit is that measurement, analysis and improvements are made from a common interest and shared point of view.
Stakeholders who normally don’t work that close together do now have an incentive to contribute to a just-in-time the system.
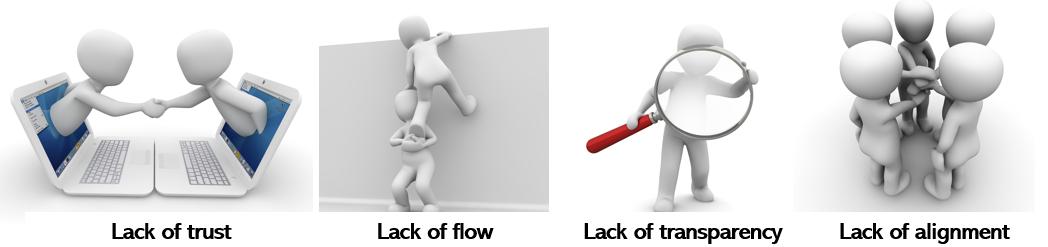
Theory of constraints
A process is as strong as its weakest link. By removing the bottlenecks, the capacity of the entire process will increase. What do you think is the biggest constraint for bringing flow on the internet? How does blockchain remove those constraints?
Lack of trust
By sharing information from the source without the need of a central authority the system becomes censorship resistant and processes become leaner. The reuse of data solves a lot of constraints in information flows.
Lack of flow
Silo-ed formation (functional, physical, geographical, product, etc.) poses the greatest risk of friction. Lean system thinking can be used to gain insight into the contributions of the fragmented parts.
Lack of transparency
Transparency becomes the new distinctive character. It solves the “bullwhip effect’, the biggest bottleneck in value transfer and prevents a lot of unnecessary work, waste and investments. It decreases the inventory and operating expenses and increases the throughput of the entire system.
Lack of alignment
Having all stakeholders and activities contribute to the common goal makes it easy to identify constraints in the network, analyze those constraints and solve them together.
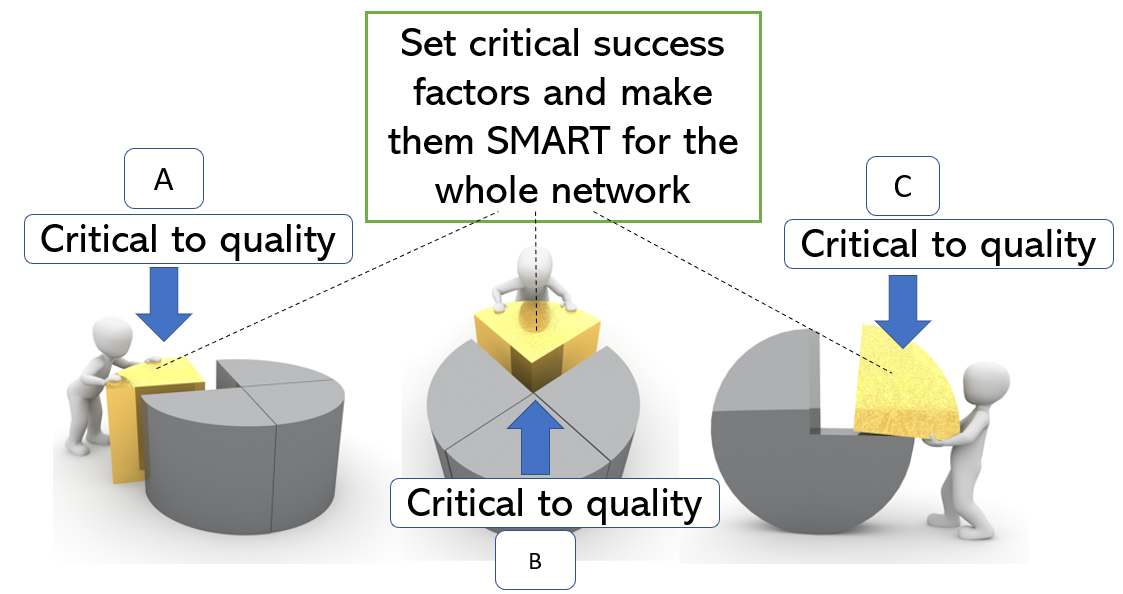
Hoshin Kanri – Shared mission and Vision
How do you create alignment with focus on quality management?
- Customer focus
- Network governance/collaboration
- Incentives/alignment for value adding activities
- End-to-end process approach (the outcome is subject to change)
- Network improvements (balancing the system),
- Direct feedbackloops (check customer fit)
- Evidence-based desicion making (smart data)
- Agility, system thinking, respond to change
Hoshin Kanri is a method to align activities and make work contribute to a shared vision and mission. How could this method be applied for a blockchain initiative? Coalition partners define what success looks like from a customer perspective and how critical to quality can be defined.
These SMART metrics “the critical success factors” should be measurable and repeatable. They mostly contribute to the input quality (first-time-right), the throughput (just-in-time) and feedback loop (customer satisfaction) and the reliability of the collaborative design (governance and sustainability). Every individual stakeholder should set key performance indicators (CtQ) that contribute to these shared goals. In order to achieve continuous improvement and alignment, the performance indicator is shared in the network. This enables other coalition partners to give feedback.
Built in quality
Built in quality is more often part of a product, process and system design.
Product design
An example of a product design is your phones’ SIM card. By cutting a corner of the card it becomes clear how to plug in the card in the mobile phone.
Process design
The google search function is a form of error prevented process design. Based on smart data analysis applications, Google knows what you will be looking for.
System design
Blockchain processes are designed as a single source of truth. There is consensus, alignment and incentives for all stakeholders in the network. With smart contracts and the use of real-time information it is possible to automatically control and improve a desired result. In traditional processes verification and control takes place afterwards, as part of the settlement.
Founders of value flow
Taiichi Ohno lived in the industrial era and is considered to be the founder of the Toyota Production System. He devised the seven wastes (muda) as part of his system thinking. These wastes are:
- Delay, waiting
- Over production
- Over processing
- Unnecessary transport (of goods, products)
- Unnecessary motion (employees)
- Inventory
- Defects
Satoshi Nakamoto is the pseudonym of an unknown person or group who designed the cryptocurrency bitcoin and founded the first blockchain database. With this invention Nakamoto was the first to solve the double-spending problem on the internet.
Now, anything of value can be digitized and exchanged on the internet without the need for a trusted third party. Peer-to-peer transactions make processes not only leaner (disintermediair), but also let us rethink what constitutes value for people and planet. The CEO of IBM expressed the possibilities of blockchain as follows: “what the internet did for information will enable blockchain for value streams”.
Lean is a management philosophy aimed at structuring the organization and processes in such a way that optimal value is created for the customer. Thanks to Taiichi, we have learned a method for extracting waste from processes. Satoshi gave us a powerful toolbox for a digital age.

5 Times Why? The lean consultant
If you have any doubts on the potential, then ask yourself the following questions:
– Why do we all keep our own records? While we know that this is one of the biggest bottlenecks for value flow.
– How do intermediaries contribute to value flows? With limited opening hours and additional costs.
– What problems can be solved with adding more transparency?
– What makes it so hard to settle the payment, process and product flows?
– How can we ensure sustainable cooperation? And trust each other.
The internet changed the way information flows. Today, we’re implementing and redesigning the way value flows. The potential of blockchain technologies, making processes more effective and efficient, is increasing. By informing and inspiring the businesses with successful use cases, the adoption of blockchain can be accelerated.
Lean thinking and lean system thinking is one of the skills needed to bring the change. Are you a lean consultant? Become part of the lean blockchain coalition!

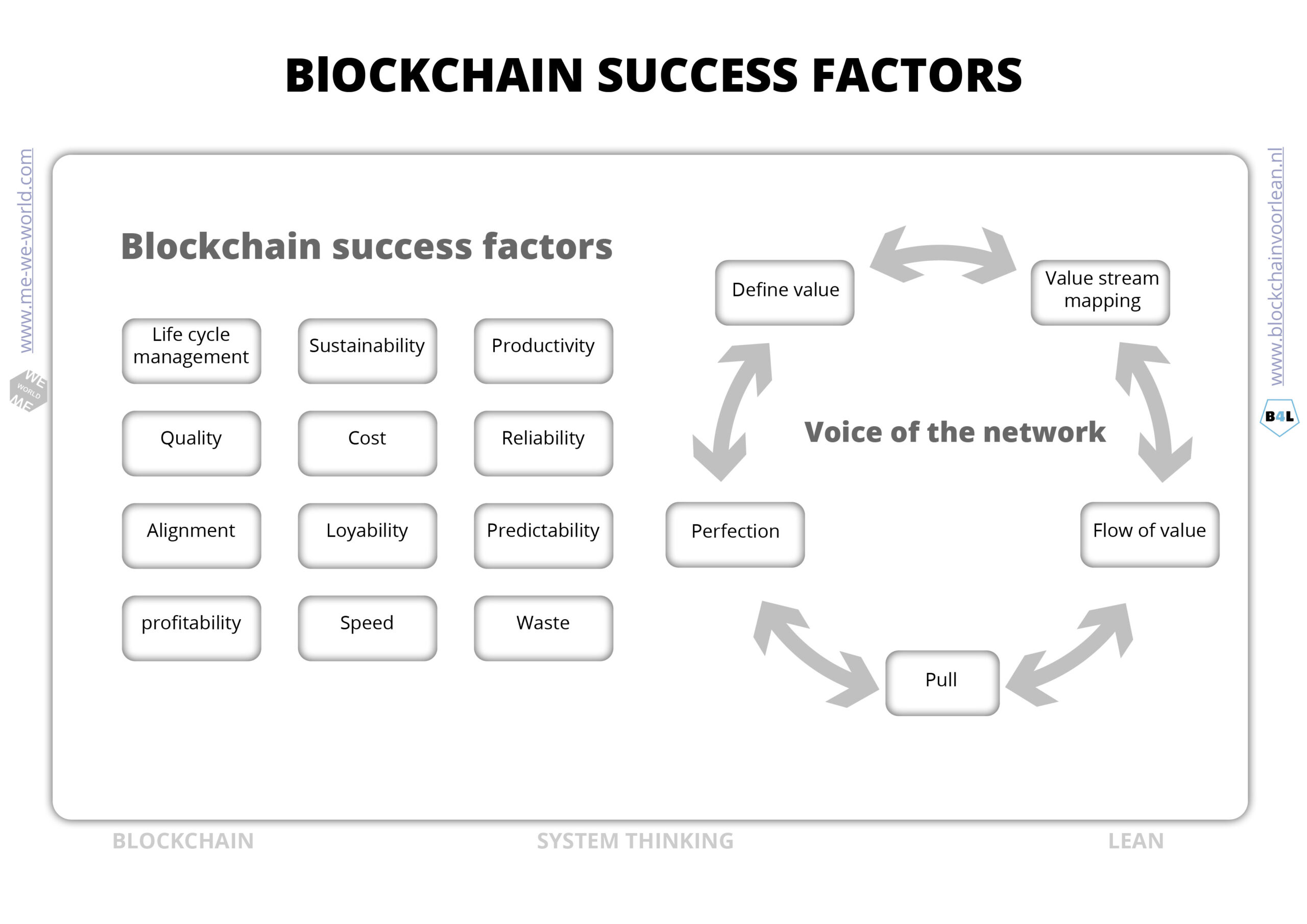
Blockchain success factors
With process optimization the focus has mainly been on lower costs, better quality, reliability, lead time and flexibility. In addition to those process optimization, we increasingly notice that other values are also become more and more important from a process optimization point of view. The dictionary of “enhancements” or “values” is slowly expanding. New “success factor metrics” includes: the reliability of the organization, the authenticity of products, origin, circularity, fair share, sustainability, etc.
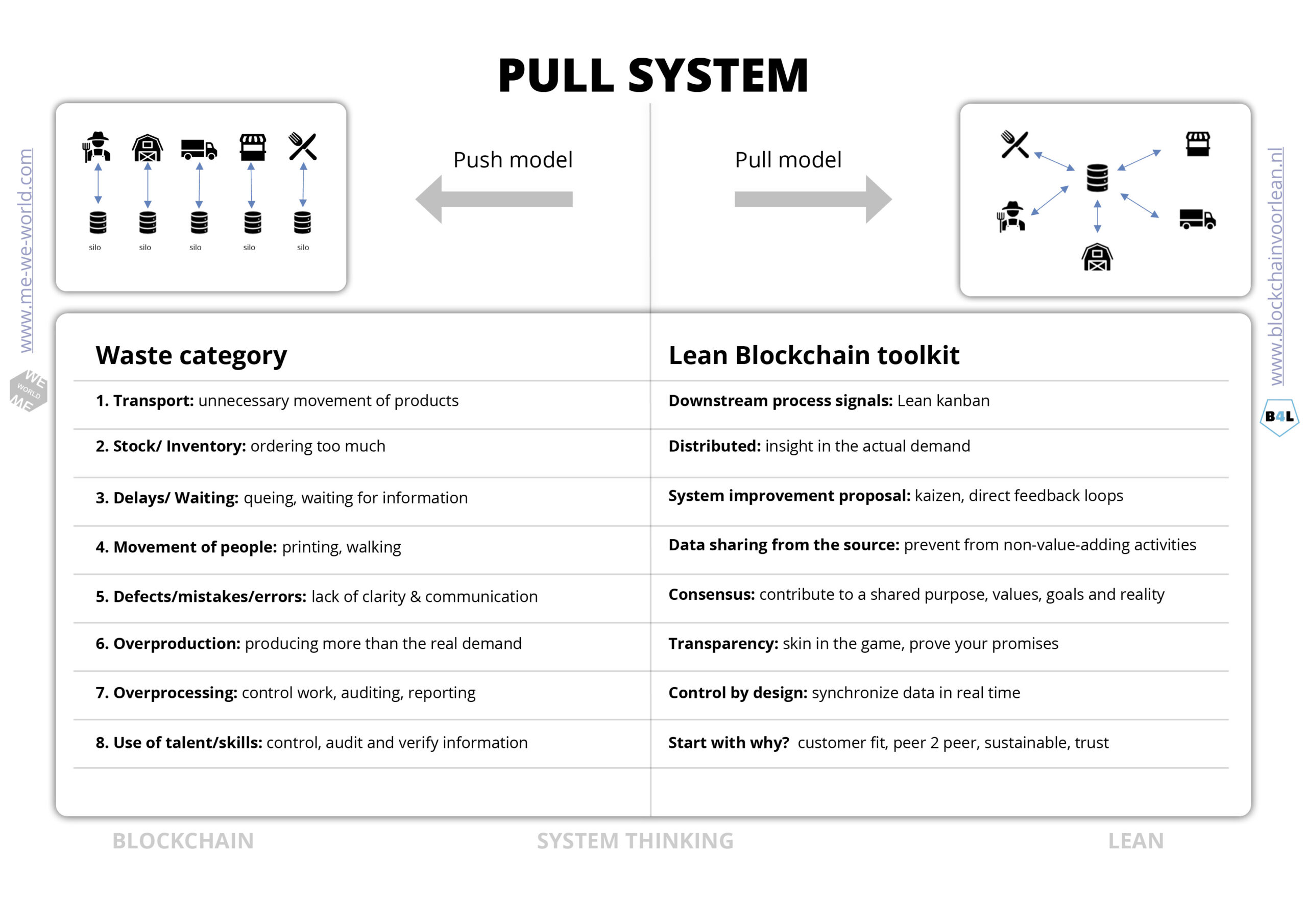
Pull system
What is a Pull system?
A pull system is a collaborative system in which production is driven by actual demand, based on shared purpose. The product or service is not ‘pushed’ through the ‘chain’, but determined on the actual demand and the need for a product. The product or service is then ‘pulled’ through the process.
What is the problem?
We face global coordination and cooperation failures. Major bottlenecks for a fruitful collaboration are often caused by the revenue models, politics, security, fragmented systems, the incentives, remuneration, power, autonomy and also ignorance.
Lean tools integated
Look at the picture below and see all the lean elements which are integrated in a Blockchain concept. Blockchain will bring new ways of governance that allow people and businesses to connect and protect their common interest. It’s a Lean system with consensus on the strategy and execution.
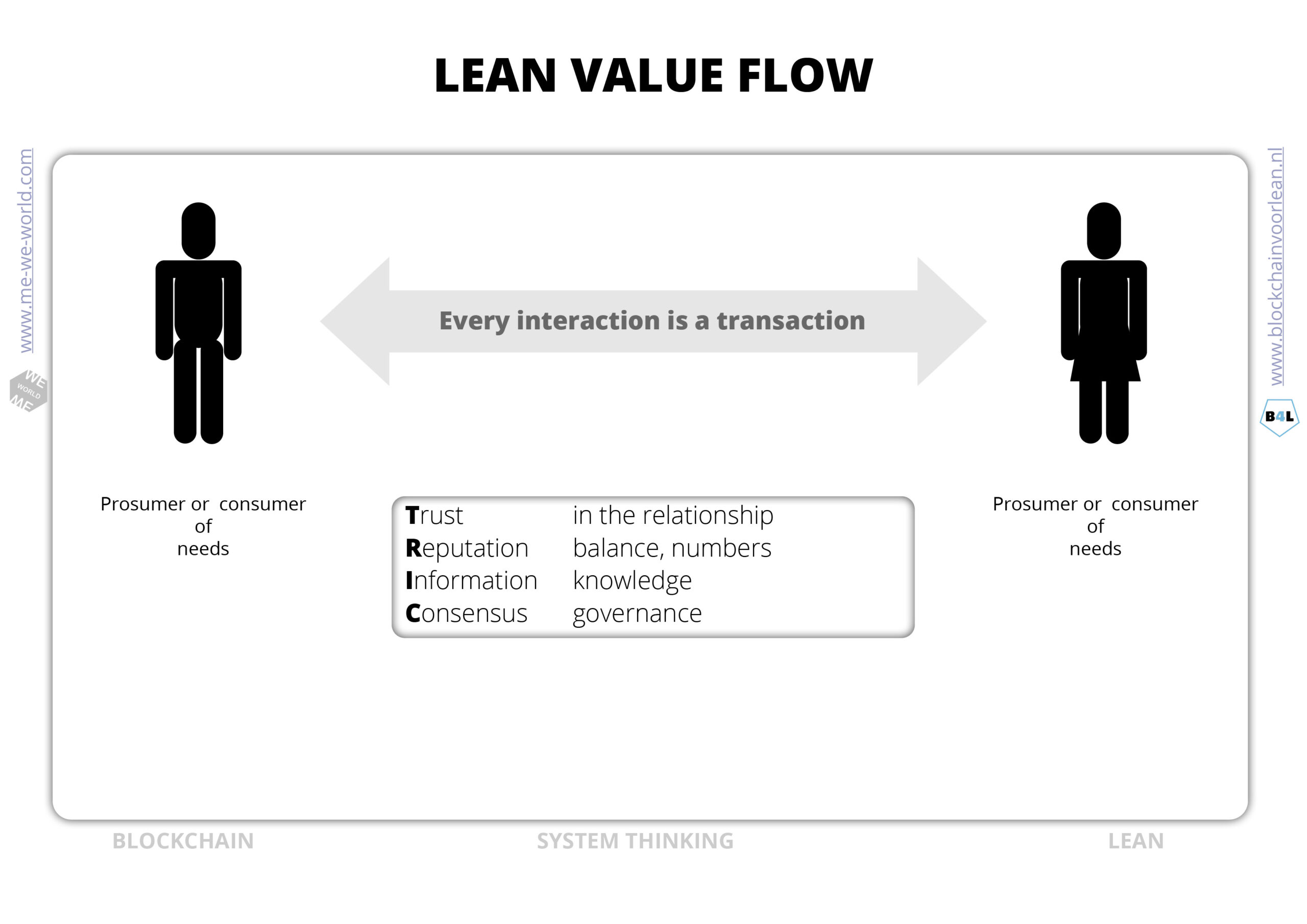
Lean value flow
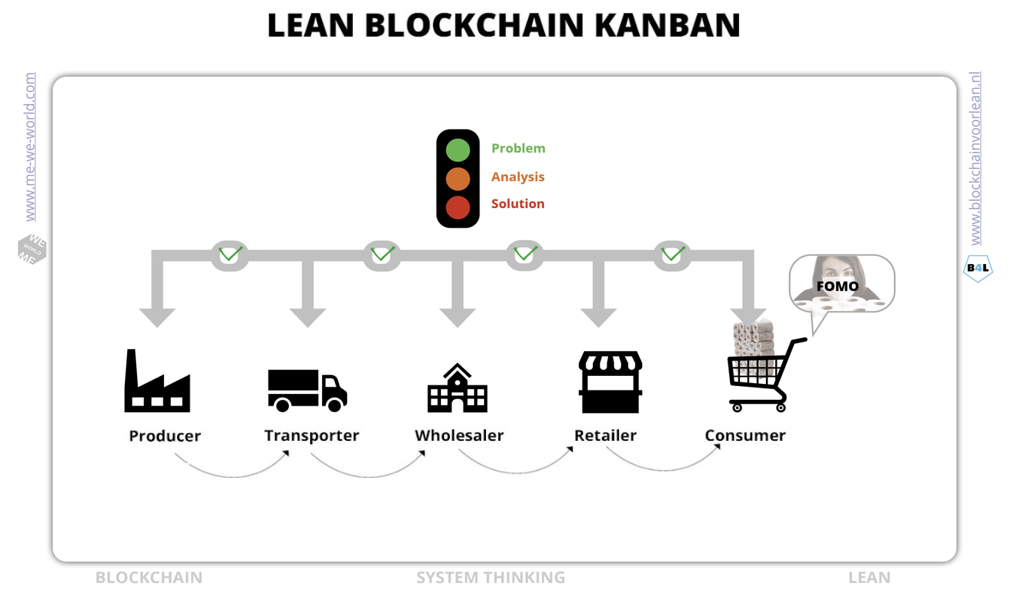
Reduce the Bullwhip Effect – Kanban
The bullwhip effect is a well-known phenomenon in supply chain. Because real-time data from actual demand is often missing, orders are placed based on estimates. An overestimation of demand leads to (unnecessary) stock (and waste), while an underestimation results in No sales at all. The cause is often found in a lack of communication and organizational inefficiency (poor cooperation). To reduce the bullwhip effect all chain members must recognize that they are part of a complex network. That each stakeholder heavily relies on the information from its direct downstream member. It’s a system of individual companies that are interlinked but disconnected. The two main causes are inaccurate information – and demand forecast. What if there is a trusted technology to share the actual demand from the source (the customers) with all stakeholders?
Five principles to reduce the bullwhip effect:
1. Share realtime information of actual demand
2. Get rid of forecasting activities
3. Design alignment, control and trust by design
4. Synchronize data, activities and operations
5. Continuos improve collaboration with direct feedbackloops
The benefits :
– Reduce order lead time and information lead time
– Lowering production costs, safety stock, transportation costs, sourcing, stock outs, storage, disposal costs etc
– Less capital destruction
– Contributing to the SDG’s (Sustainable Development Goals)
– Improved customer fit and service